CLASSES AND USES
COMMON CEMENTS (CEM Prefix) UNE-EN 197-1: 2000 Standard
TYPE I CEMENT
Portland without major addition
| Notation | Designation | Main addition |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||
| Portland cement | CEM I | – | – |
Main fields of application:
Concretes and prefabricated high or very high strength. Special public works of pre-stressed concrete.
Most important contraindications:
Works in aggressive environments. Concrete works of great volume or thickness and structures easily crackable by retraction.
TYPE II/A CEMENT
Portland con bajo contenido de adición principal
| Designation | Notation | Main addition |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||
| Portland Slag Cement | CEM II/A-S | S | 6-20 |
| Portland Silica Fume Cement | CEM II/A-D | D | 6-10 |
| Portland Natural Pozzolana Cement | CEM II/A-P | P | 6-20 |
| Portland Industrial Pozzolana Cement | CEM II/A-Q | Q | 6-20 |
| Portland Siliceous Fly Ash Cement | CEM II/A-V | V | 6-20 |
| Portland Calcareous Fly Ash Cement | CEM II/A-W | W | 6-20 |
| Portland Burnt Shale Cement | CEM II/A-T | T | 6-20 |
| Portland Limestone Cement | CEM II/A-L | L | 6-20 |
| CEM II/A-LL | LL | 6-20 | |
| Portland Composite Cement | CEM II/A-M | S/D/P/Q/T/W/L/LL | 12-20 |
Main fields of application:
Concretes, prefabricated and mortars in general, high or medium strength.
Most important contraindications:
Works in aggressive environments, although it will depend on the type and amount of addition.
TYPE II/B CEMENT
Portland with moderate main addition content
| Designation | Notation | Main addition | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||
| Portland Slag Cement | CEM II/B-S | S | 21-35 |
| Portland Natural Pozzolana Cement | CEM II/B-P | P | 21-35 |
| Portland Industrial Pozzolana Cement | CEM II/B-Q | Q | 21-35 |
| Portland Siliceous Fly Ash Cement | CEM II/B-V | V | 21-35 |
| Portland Calcareous Fly Ash Cement | CEM II/B-W | W | 21-35 |
| Portland Burnt Shale Cement | CEM II/B-T | T | 21-35 |
| Portland Limestone Cement | CEM II/B-L | L | 21-35 |
| CEM II/B-LL | LL | 21-35 | |
| Portland Composite Cement | CEM II/B-M | S/D/P/Q/T/W/L/LL | 21-35 |
Main fields of application:
Concretes and mortars in general, especially of medium or low strength.
Most important contraindications:
Works in aggressive environments, although it will depend on the type and amount of addition.
TYPE III CEMENT
Blastfurnace cement
| Designation | Notation | Main addition |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||
| Blastfurnace cement | CEM III/A | S | 36-65 |
| CEM III/B | 66-80 | ||
| 81-95 | |||
Main fields of application:
Concretes in aggressive environments (sulfates present in the ground, aggressive waters and sea, etc.). Equivalent to SR type.
Most important contraindications:
Works in which an appropriate care can not be assured or aesthetics are important. Concrete at low temperatures.
Low early strength blastfurnace cement Suffix L UNE-EN 197-1: 2011
| Designation | Notation | Main addition |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||
| Low early strength blastfurnace cement | CEM III/A-L | S | 36-65 |
| CEM III/B-L | 66-80 | ||
| CEM III/C-L | 81-95 | ||
Main fields of application:
The same as the blastfurnace, but when the works are massive (compacted concrete dams).
Most important contraindications:
The same as the blastfurnace.
TYPE IV CEMENT
Puzzolanic cement
| Designation | Notation | Main addition |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||
| Puzzolanic cement | CEM IV/A | D/P/V | 11-35 |
| CEM IV/B | 36-55 | ||
Main fields of application:
Concretes and mortars in general, especially in moderately aggressive environments by pure waters, weakly acidic or aggressive carbonic. Concrete for water works. Concretes with aggregate reactive with alkalis.
Most important contraindications:
Works in very aggressive environments.
TYPE V CEMENT
Composite cement
| Designation | Notation | Main addition |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||
| Composite cement | CEM V/A | S/P/Q/V | 18-30 |
| CEM V/B | 31-49 | ||
Main fields of application:
Stabilization of soils. Soil cement, cement-bound graded aggregate and pavement structural layers. Dry and compacted concrete for dams or large masses.
Most important contraindications:
Not recommended in any other cases.
OTHER CEMENTS
VERY LOW HEAT SPECIAL CEMENTS
Prefix VHL UNE-EN 14216:2005
| Designation | Notation | Main addition |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||
| Blastfurnace cement | CEM III/B-L | S | 66-80 |
| CEM III/C | 81-95 | ||
| Puzzolanic cement | CEM IV/A-L | D/P/Q/V/W | 11-35 |
| CEM IV/B | 36-65 | ||
| Composite cement | CEM V/A-L | S/P/Q/V | 18-30 |
| CEM V/B | 31-50 | ||
Main fields of application:
The same as the corresponding CEM, but when the works are massive (compacted concrete dams).
Most important contraindications:
The same as the corresponding CEMs.
WHITE PORTLAND CEMENT (WOPC)
Prefix BL UNE 80305:96
| Designation | Notation | Main addition | Main fields of application | Most important contraindications | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||||
| Portland white cement (WOPC) | BL I | S/D/P/Q/T/W/L/LL | 0-5 | Concretes and prefabricated concretes with high or very high resistances. Special mortars (monolayer) | Analogous to CEM I y CEM II cements |
| Portland white cement (WOPC) with additives | BL II | S/D/P/Q/T/W/L/LL | 6-25 | Concretes and prefabricated concretes with high or medium resistances. Special mortars (monolayer) | |
| Portland white cement (WOPC) for tiling | BL V | S/D/P/Q/T/W/L/LL | 26-60 | Tiling, pavements, lining, plasters, masonry, etc. | Prohibited for structures |
SPECIAL CEMENTS
Prefix ESP UNE 80307:2001
| Designation | Notation | Main addition |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||
| Cements for special uses | ESP VI-1 | S/P/V | 45-75 |
Main fields of application:
Analogous to CEM V cements and especially in road pavements (pavements, bases, subbases) and in dams.
Most important contraindications:
Not recommended in any other cases.
CEMENTS WITH ADDITIONAL CHARACTERISTICS
Suffixes
| Designation | Notation | Main fields of application | Most important contraindications | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNE 80303-1:2013 | Sulfate resistant | /SR | Sulfate or seawater presence.Foundations in gypsum rich soils. Maritime works in particularly aggressive environments | According to the corresponding type and subtype of cement |
| UNE 80303-1:2013 | Seawater resistant | /MR | Contact with seawater. Maritime works | |
| UNE-EN 197-1:2011 | Low heat of hydration (slow reacting) | /BC | Low shrinkage concrete. Concrete in warm weather. Large masses of concrete (dams) | |
MASONRY CEMENTS
UNE-EN 413-1:2005
| Designation | Notation | Main addition |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||
| MC 5 | S/D/P/Q/T/W/L/LL | ≤ 75 | |
| MC 12,5 | |||
| MC 12,5 X | ≤ 60 | ||
| MC 22,5 X | |||
Main fields of application:
Masonry mortars.
Most important contraindications:
Not recommended in any other cases.
CEMENTS OF CALCIUM ALUMINUM
CAC/R UNE-EN 14647:2006
| Designation | Notation | Main addition |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | % by mass | ||
| Calcium aluminum cements | CAC/R | Composed only of calcium aluminate without any addition | |
Main fields of application:
Concretes and refractory mortars. Aggressive media (sulfates, sea water or weak acid) and in general for specific practices.
Most important contraindications:
Not recommended in any other cases.
STRENGTH CLASS
| Type of cement | Class strength | Compressive strength (N/mm2) | ||||||
| Initial | Normalized (28 days) | 90 days | ||||||
| 6 h | 24 h | 2 days | 7 days | Min. | Max. | |||
| CEM and SR/MR | 52,5 R | 30,0 | 52,5 | |||||
| CEM BL and SR/MR | 52,5 (N) (*) | 20,0 | 52,5 | |||||
| CEM BL and SR/MR | 42,5 R | 20,0 | 42,5 | 62,5 | ||||
| CEM BL and SR/MR | 42,5 (N) (*) | 10 (***) 10 (**) |
42,5 | 62,5 | ||||
| CEM and SR/MR | 32,5 R | 10 (**) | 32,5 | 52,5 | ||||
| CEM and SR/MR | 32,5 (N) (*) | 16 | 32,5 | 52,5 | ||||
| BL | 22,5 X (**) | 22,5 | 42,5 | |||||
| ESP | 42,5 (N) (**) | 22,5 | 52,5 | 42,5 | ||||
| ESP | 32,5 (N) | 32,5 | 42,5 | 32,5 | ||||
| ESP | 22,5 (N) | 12,5 | 32,5 | 22,5 | ||||
| MC | MC 5 (**) | 5,0 | 15,0 | |||||
| MC | MC 12,5 (X) (**) | 7,0 | 12,5 | 32,5 | ||||
| MC | MC 22,5 (X) (**) | 10 | 22,5 | 42,5 | ||||
| CAC/R | 18,0 | 40,0 | ||||||
The compression depends mainly on three factors:
- The fineness of the grinding operation
- The mixture of clinker, gypsum and additions
- The proportions of these materials
Legend:
R: High early strength
(*) N: Normal early strength according to UNE-EN 197-1
(**) Minimum strength 2 days according to UNE-EN 197-1
(***) According to RC-16 and the regulation of the N mark quality certification for cements
APPLICATIONS OF EACH TYPE OF CEMENT
The special characteristics of each cement, type and strength class, make it more or less suitable for the different types of works or, more specifically, for the requirements of each class of concrete.
As a guideline, the following table gives some general indications as to the suitability of each cement for each primary use or class of concrete. For a more accurate knowledge of the applications, and to identify the suitability of each cement for each type of work (foundations, pavements, structures, maritime works, etc.), annex VIII of the INSTRUCTION FOR THE RECEPTION OF CEMENTS RC-16 can be consulted.
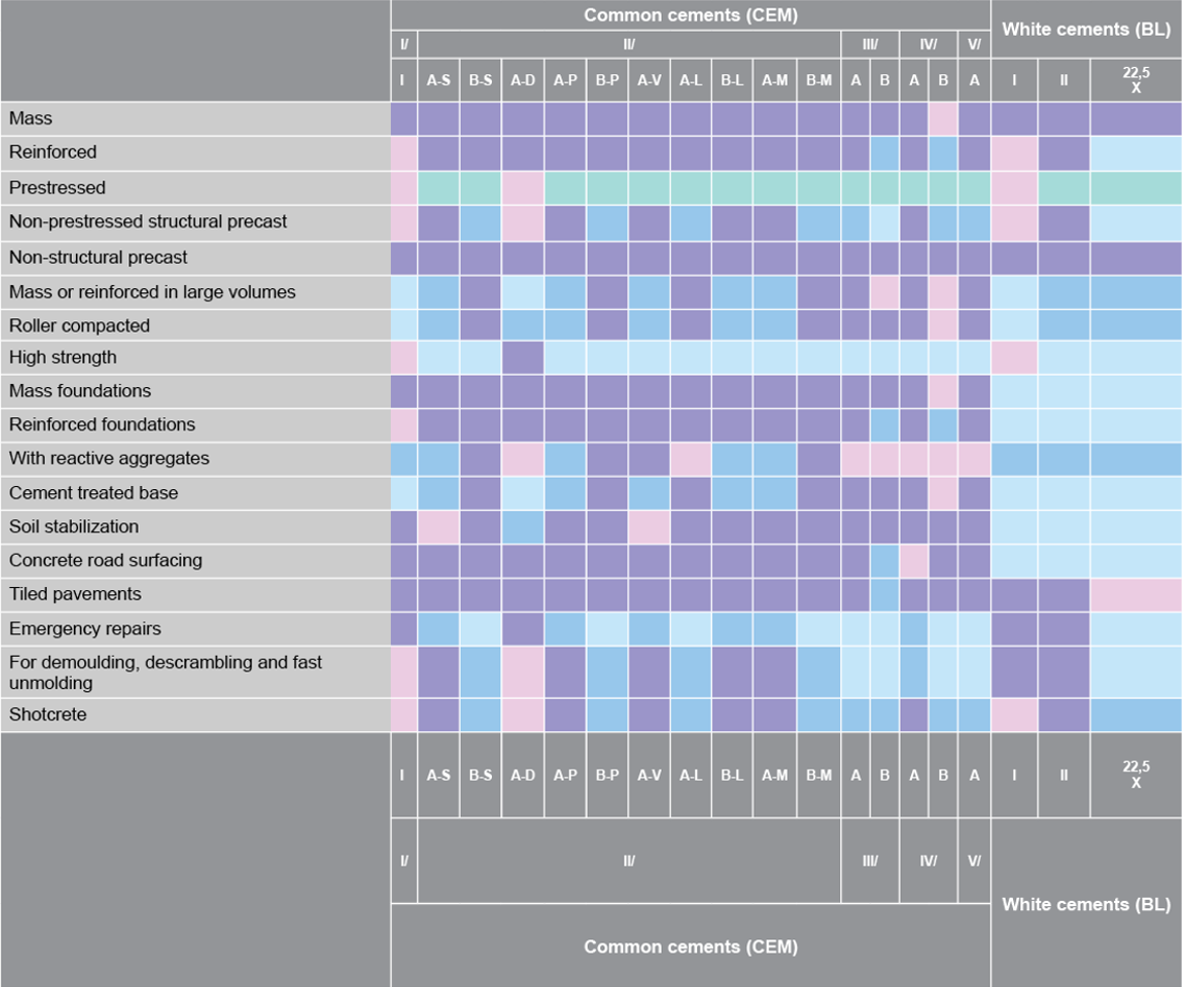
- ESP VI-1 Only use, in certain grade, in large masses of concrete.
- /SR o /MR Usable in certain grades, according to type and category, in any concrete or structural element that must withstand sulfate (SR) or seawater (MR) attacks.
- /BC Usable in certain grades, according to type and category, in mass or reinforced concrete requiring low heat of hydration.
- CAC/R Usable in certain grades in:
- Refractory mortars and mortar
- Mass concrete and mortars in aggressive media by sulfates, sea water or slightly acidic waters.
Not usable in pre-stressed concrete and pre-stressed prefabricated structural elements.
